I Rosenberg's description of Hjortspring Fundet indicates the types of wood used for the boat. These are described belowr.
Lime tree
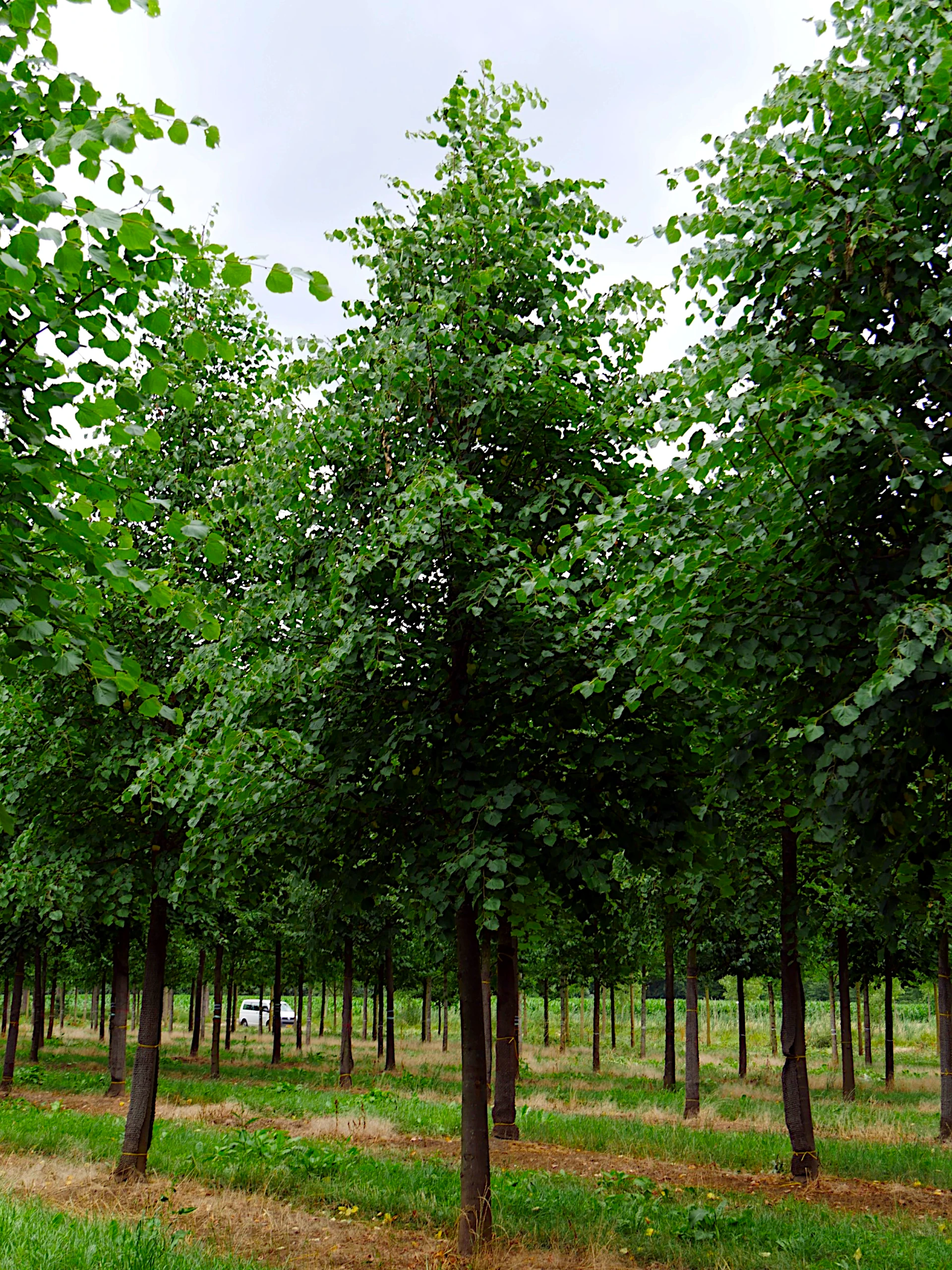
Linden is the primary wood species used to build the Tilia's hull.
The five planks
Tilia platyphyllos
The requirement for the planks is that the bottom 19 metres must be without side branches. Such trees are difficult to find in Denmark, so they were found, and bought, in Poland. We bought three and got four, the last one was damaged during felling.
For the trunks to reach the desired length, they need to grow relatively densely in a forest.
Of the planks we produced, there was only one knot from a broken branch hidden inside the log. The knot was removed and lime plug glued in its place.
Other name: Large-leaved lime.
Description:
The tree is up to 30 metres tall,
deciduous tree with an initially spherical, later tall cylindrical crown. The trunk is strong and straight with ascending main branches.
It has hairy petioles and annual shoots.
The leaves are 6-12 cm long (without stem), almost round to oval and have an oblique heart-shaped base. They have a distinct tip and a sharply serrated edge. The upper side is hairy and dark green, while the underside is pale green with dense hair along the nerves.
Where: Large-leaved lime grows on moist and nutrient-rich soil in Central and Southern Europe. Here it forms (along with other deciduous trees) the final stage of thousands of years of forest development. In Denmark, it is probably only found as a native species on islands and in isolated forests in the south of the country. It is planted in parks and avenues.
Source: Wikipedia
Tilia cordata
For the two ships' bows, we used local linden wood. We don't need tall trunks, but strong ones because they need to be able to hold the entire stem block and preferably also the upper horn. However, we were unable to fulfil the latter requirement.
Other names: Small-leaved lime, Scots lime, (often confused with park lime, a cross between small- and large-leaved lime).
Description:
A tree up to 30 metres tall with a broad conical growth form. The trunk is short and thick and divides quickly into a number of competing top shoots. The main branches are broadly overhanging with upturned tips.
The leaves are round to obliquely heart-shaped with a finely serrated margin and short tip. The upper side is dark green, while the underside is blue (grey) green.
Petioles and annual shoots completely hairless.
Where: The tree is the second longest-lived Danish tree after the oak and used to be among the most common forest trees in Denmark.
Until the Bronze Age, it was one of the most common forest trees in Denmark, and until the middle of the 7th century it was the small-leaved lime that had the place in the deciduous forest that beech has now taken over.
Source: Wikipedia.
Ash
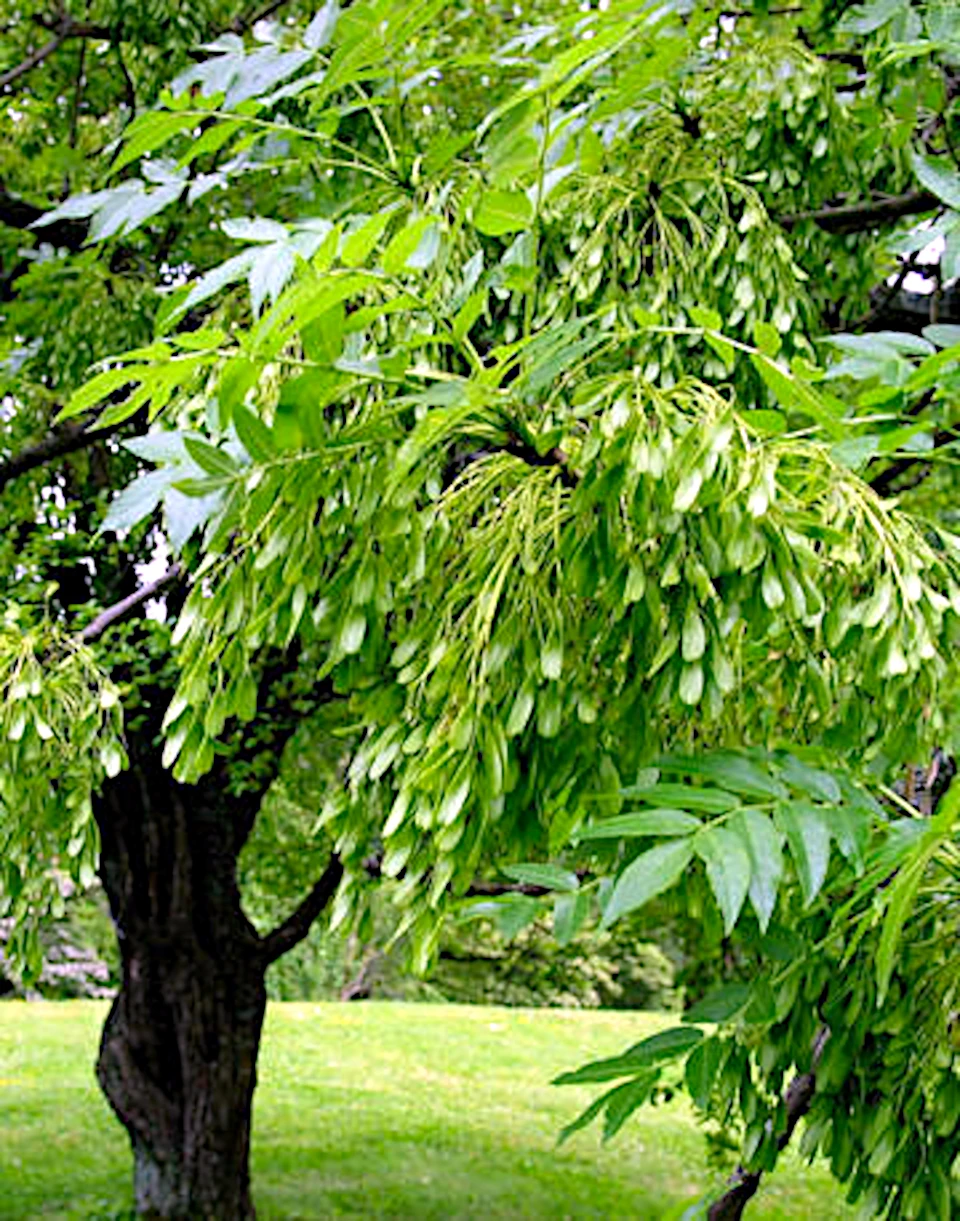
Fraxinus excelsior
Ash is used for the ribs, as the deck beams and pillars are made from this wood. We later used mirror-split ash wood for the boat's decks, which were made of linden boards, but they were too weak for adults.
Description:
Common ash is a tree up to 35 metres tall that grows on moist ground in forests and scrub. It is often planted. Ash has an open crown and light foliage that lets a lot of light through.
The leaves of the ash tree are compound. One leaf is on average 25 cm long.
Ash is a large, deciduous tree with a tall and open growth form. The crown is slender and conical at first, but later becomes more flat and domed (especially in female trees). The trunk is straight and continuous to the top. The main branches are first ascending, then more spreading and finally overhanging.
Where: Ash is found in light-coloured mixed forests throughout Western Europe (including Denmark) where there is abundant rainfall or high and nutrient-rich groundwater. It thrives in both light and some shade and does well on all types of soil, though best on nutrient-rich, fairly moist and calcareous topsoil. Ash does not tolerate stagnant water in the soil. However, the tree tolerates wind and salt. It is common throughout Denmark, with the exception of West Jutland.
Source: Wikipedia.
Oak tree
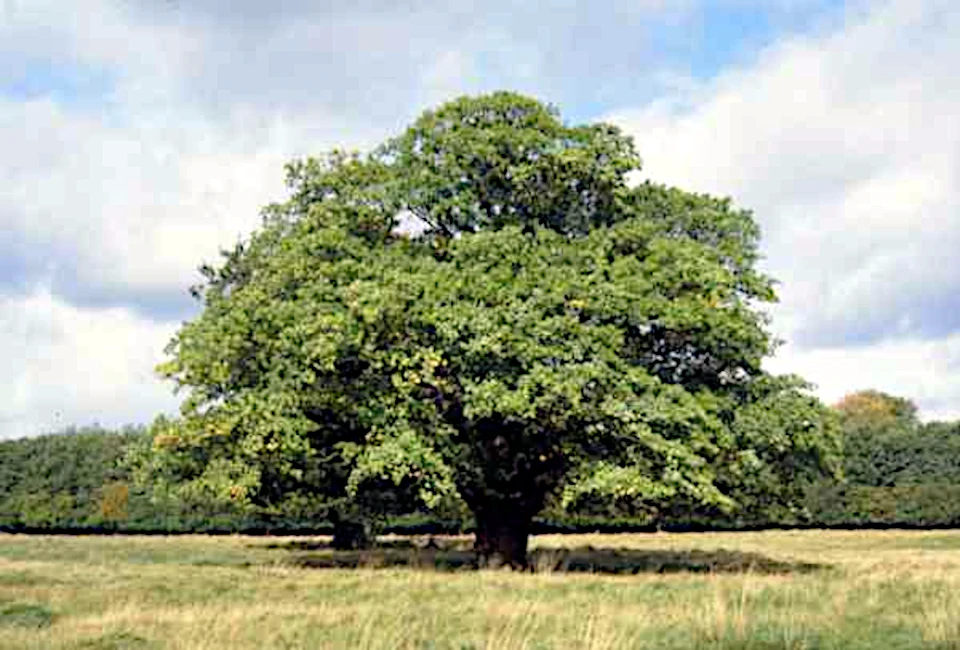
Quercus
In Tilia, we have used oak as the stem wood to connect the stem block firmly to the bottom plank and as support between the railing and keel horns, also called outer locking pieces. In addition, all square nails, 7 at each end, are made of oak.
Description:
Oak is a genus of trees and shrubs with about 600 species mostly distributed in the temperate and subtropical parts of the northern hemisphere.
Oak wood is often used for heavy constructions such as harbour piers, building timbers (including roof structures), bridges and ships. Many of the great Viking ships were made of oak, including Skuldelev 2, the Oseberg Ship and the Kolding Cog. Many oak forests around Denmark were planted around 1800 when large naval constructions and harbour expansions were planned.
Where: Oak survived the last ice age in southern Europe. Oak has been in Denmark since the beginning of the Atlantic Warm Period, around 7000 BC. Oak came to Norway around 5000 BC. In the warm period 5500-500 BC, oak was much more widespread than today. Around 1,500 species of insects, fungi, mosses and lichens have been found on oak; wood-mould formed inside the cavity of a hollow oak tree provides a highly nutritious base for many rare insect species. During the 17th century, the large oak forests partially disappeared due to shipbuilding and land cultivation.
Source: Wikipedia.
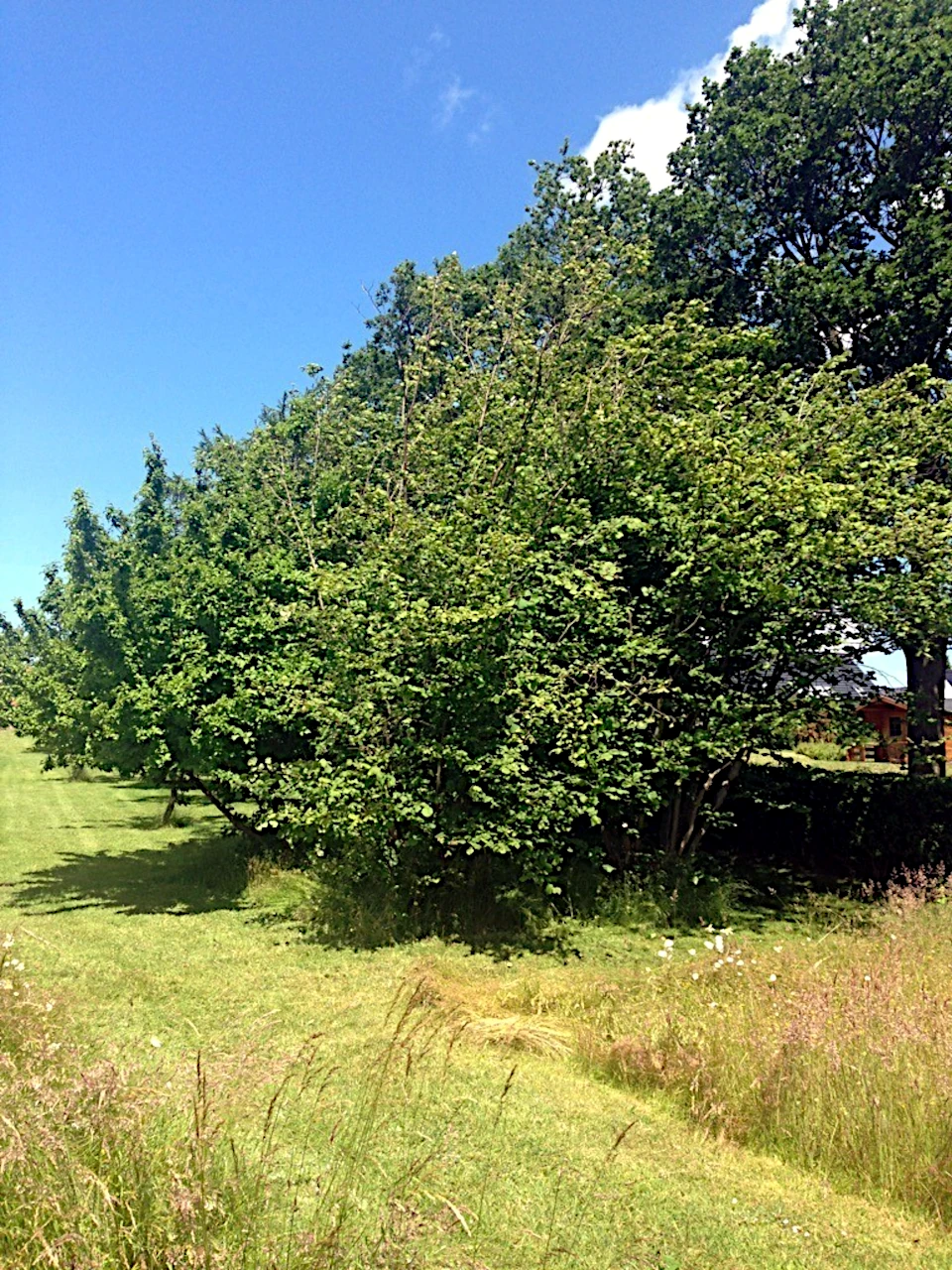
Hazel
Corylus avellana
Hazel branches are used as frames in the rib racks when stripped of bark. They are also used for our two poles and boat hook, however, these are not part of the find, but necessary for our use of Tilia.
Description:
Hazel, also called wood hazel, is a multi-stemmed shrub, usually 3-5 metres tall, of the birch family, native to Europe and Asia. It can sometimes become almost woody with an umbrella-shaped crown and has been reported up to 15 metres in size.
Where: Hazel is found throughout Europe on moist and mineral-rich soils, forming thickets, forest edges and undergrowth in lush oak mixed forests.
Hazelnuts are a nutritious and tasty food, which is why hazel is cultivated as a crop.
Source: Wikipedia.
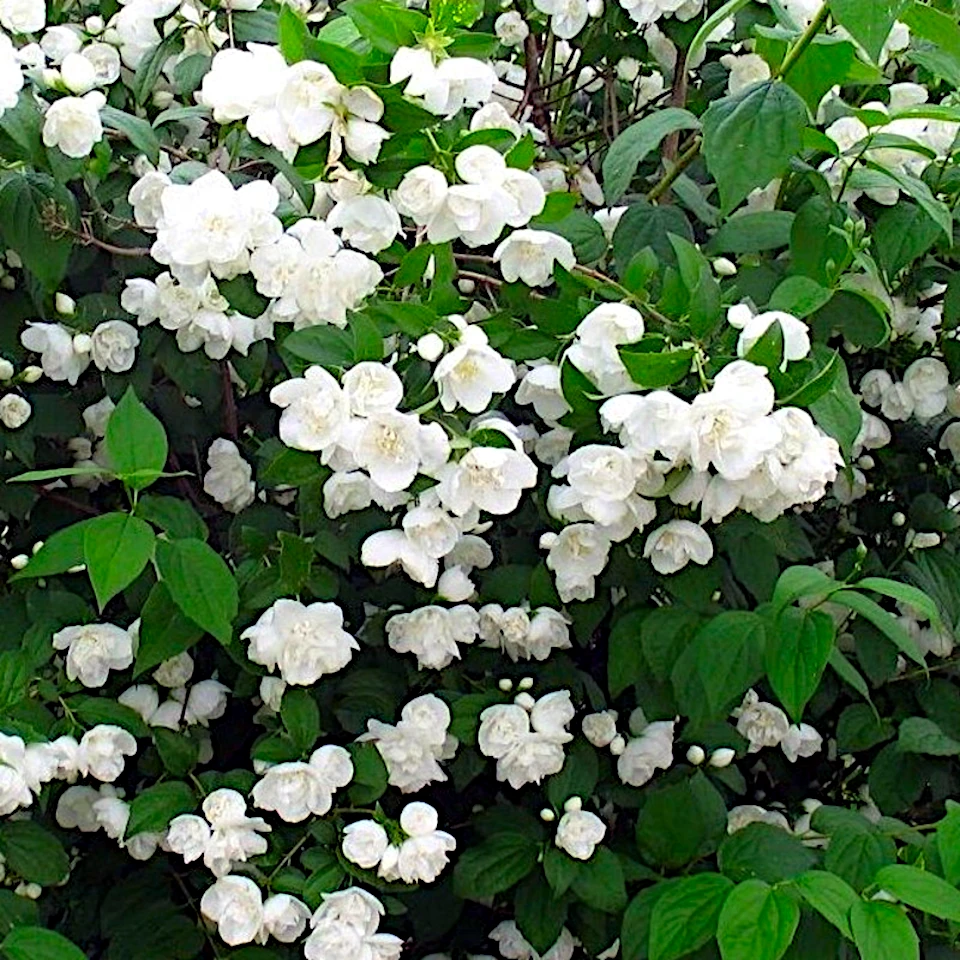
Fake jasmine
Philadelphus coronarius
Rosenberg described the discovery of one (or more) bundles of thin branches, about 10 mm in diameter and about 1 metre long. He did not describe what these bundles could have been used for. We have chosen to place several bundles in the two, 2 metre long, boat compartments in front of toft 10 and aft of toft 1. At the front, they are used as a footrest for the two paddlers, you can't paddle with your feet floating in the air. At the same time, personal goods can be stored here, keeping them clear of the bottom water. Likewise in the aft boat compartment. Here, goods such as food can be placed on the branches during lifting and provide a safe surface for the mate.
The bundles are of a suitable diameter and held together with bast cords.
The branches of this shrub are only chosen because it is found in many gardens and still needs to be pruned every year, removing the oldest branches.
Description:
Is a large, deciduous shrub with a growth form that is stiff-branched and upright. Also known as fragrant pipewood, it is an old, well-known ornamental shrub with snow-white, fragrant flowers. The branches have white pith.
The flowers appear in June-July and are in short clusters from the leaf corners. They are white with yellow stamens. The scent is sweet and strong.
Source: Wikipedia.